先看一个实例,在下面的程序中可以传入一个对象,以及要反射调用的方法和方法的参数:
public static <T>Future<T> getFuture(final Object t, final String methodName, final Object... dto) {
Callable callable = new Callable() {
@Override
public Object call() throws Exception {
Object result = null;
Method[] methods = t.getClass().getMethods();
for (Method m : methods) {
if (methodName.equalsIgnoreCase(m.getName())) {
try {
result = m.invoke(t, dto);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
// 获取实际目标异常
Throwable targetException = e.getTargetException();
log.error(methodName+"【Future】执行异常:"+targetException);
throw e;
}
}
}
return result;
}
};
return executor.submit(callable);
}这里有一个注入对象
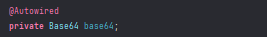
现在想通过反射base64这个对象并调用get64这个方法

但是执行之后返回的结果是null,说明调用失败了。但是通过@Autowire注入的mapper却可以调用,这里就很奇怪了。
同样是注入对象,为什么一个能调用,一个无法调用呢?
后面查询到原来mybatis的mapper是jdk代理的,而被@Component,@Service等修饰的对象注入是由CGLIB代理的,所以反射出来的对象无法调用原本的方法,只能获取原对象去进行调用。
更改后的代码:
public static <T>Future<T> getFuture(final Object t, final String methodName, final Object... dto) {
Callable callable = new Callable() {
@Override
public Object call() throws Exception {
Object target = t;
if (AopUtils.isAopProxy(target)) {
target = AopProxyUtils.getSingletonTarget(target);
}
Object result = null;
Method[] methods = target.getClass().getMethods();
for (Method m : methods) {
if (methodName.equalsIgnoreCase(m.getName())) {
try {
result = m.invoke(target, dto);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
// 获取实际目标异常
Throwable targetException = e.getTargetException();
log.error(methodName+"【Future】执行异常:"+targetException);
throw e;
}
}
}
return result;
}
};
return executor.submit(callable);
}可以看到,我们通过AopUtils这个类的isAopProxy方法去验证是否是cglib代理的对象
isAopProxy源码:
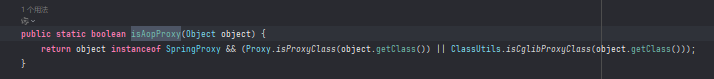
如果是CGLIB代理对象则通过AopProxyUtils.getSingletonTarget方法去获取原对象,此时再使用invoke调用方法则调用成功
发表回复